Carbon Capture And Storage Reading Answer
IELTS Academic Reading Passage
Could better design cure our throwaway culture?
A
Jonathan Chapman, a senior lecturer at the University of Brighton, UK, is one of a new breed of “sustainable designers’. Like many of us, they are concerned about the huge waste associated with Western consumer culture and the damage this does to the environment. Some, like Chapman, aim to create objects we will want to keep rather than discard. Others are working to create more efficient or durable consumer goods or goods designed with recycling in mind. The waste entailed in our fleeting relationships with consumer durables is colossal
B
Domestic power tools, such as electric drills, are a typical example of such waste. However much DIY the purchaser plans to do, the truth is that these things are thrown away having been used, on average, for just ten minutes. Most will serve conscience time, gathering dust on a shelf in the garage; people are reluctant to admit that they have wasted their money. However, the end is inevitable for thousands of years in landfill waste sites. In its design, manufacture, packaging, transportation, and disposal, a power tool consumes many times its own weight in resources, all for a shorter active lifespan than that of the average small insect.
C
To understand why we have become so wasteful, we should look to the underlying motivation of consumers. ‘People own things to give expression to who they are and to show what group of people they feel they belong to’ Chapman says. In a world of mass production, however, that symbolism has lost much of its potency. For most of human history, people had an intimate relationship with objects they used or Often they made the objects themselves, or family members passed them on. For more specialist objects, people relied on expert manufacturers living close by, whom they probably knew personally. Chapman points out that all these factors gave objects a history – a narrative – and an emotional connection that today’s mass production cannot match. Without these personal connections, consumerist culture instead of idolizes novelty. We know we can’t buy happiness, but the chance to remake ourselves with glossy, box-fresh products seems irresistible. When the novelty fades we simply renew the excitement by buying more new stuff: what John Thackara of Doors of Perception, a network for sharing ideas about the future of design, calls the “schlock of the new”.
D
As a sustainable designer, Chapman’s solution is what he calls “emotionally durable design”. Think about your favourite old jeans. They just don’t have the right feel until they have been worn and washed a hundred times, do they? It is like they are sharing your life story. You can fake that look, but it isn’t the same. Chapman says the gradual unfolding of a relationship like this transforms our interactions with objects into something richer than simple utility. Swiss industrial analyst Walter Stahel, visiting professor at the University of Surrey, calls it the “teddy-bear factor”. No matter how ragged and worn a favourite teddy becomes, we don’t rush out and buy another one. As adults, our teddy bear connects us to our childhoods, and this protects it from obsolescence Stahel says this is what sustainable design needs to do.
E
It is not simply about making durable items that people want to keep. Sustainable design is a matter of properly costing the whole process of production, energy use, and disposal. “It is about the design of systems, the design of culture,” says Tim Cooper from the Centre for Sustainable Consumption at Sheffield Hallam University in Britain. He thinks sustainable design has been “surprisingly slow to take off” but says looming environmental crises and resource depletion are pushing it to the top of the agenda.
F
Thackara agrees. For him, the roots of impending environmental collapse can be summarized in two words: weight and speed. We are making more stuff than the planet can sustain and using vast amounts of energy moving more and more of it around ever faster. The Information Age was supposed to lighten our economies and reduce our impact on the environment, but the reverse seems to be happening. We have simply added information technology to the industrial era and hastened the developed world’s metabolism, Thackara argues.
G
Once you grasp that, the cure is hardly rocket science: minimize waste and energy use, stop moving stuff around so much and use people more. EZIO MANZINI, Professor of industrial design at Politecnico di Milano University, Italy, describes the process of moving to a post-throwaway society as “changing the engine of an aircraft in mid-flight’ Even so, he believes it can be done, and he is not alone.
H
Manzini says a crucial step would be to redesign our globalized world into what he calls the “multi-local society”. His vision is that every resource, from food to electricity generation, should as far as possible be sourced and distributed locally. These local hubs would then be connected to national and global networks to allow the most efficient use and flow of materials.
I
So what will post-throwaway consumerism look like? For a start, we will increasingly buy sustainably designed products. This might be as simple as installing energy-saving light bulbs, more efficient washing machines, or choosing locally produced groceries with less packaging.
J
We will spend less on material goods and more on Instead of buying a second car, for example, we might buy into a car-sharing network. We will also buy less and rent a whole lot more: why own things that you hardly use especially things that are likely to be updated all the time? Consumer durables will be sold with plans already in place for their disposal. Electronic goods will be designed to be recyclable, with the extra cost added to the retail price as prepayment. As consumers become increasingly concerned about the environment, many big businesses are eagerly adopting sustainable design and brushing up their green credentials to please their customers and stay one step ahead of the competition.
Questions 1-2
Choose the correct letter A, B, C, or D.
Write the correct letter in boxes 1-2 on your answer sheet.
1. What is the global average for electricity generated from coal?
A 41%
B 44%
C 49%
D 70%
2. What does the average American pay each month for CO2 produced by a local power plant?
A $17
B $80
C $113
D Nothing
Questions 3-8
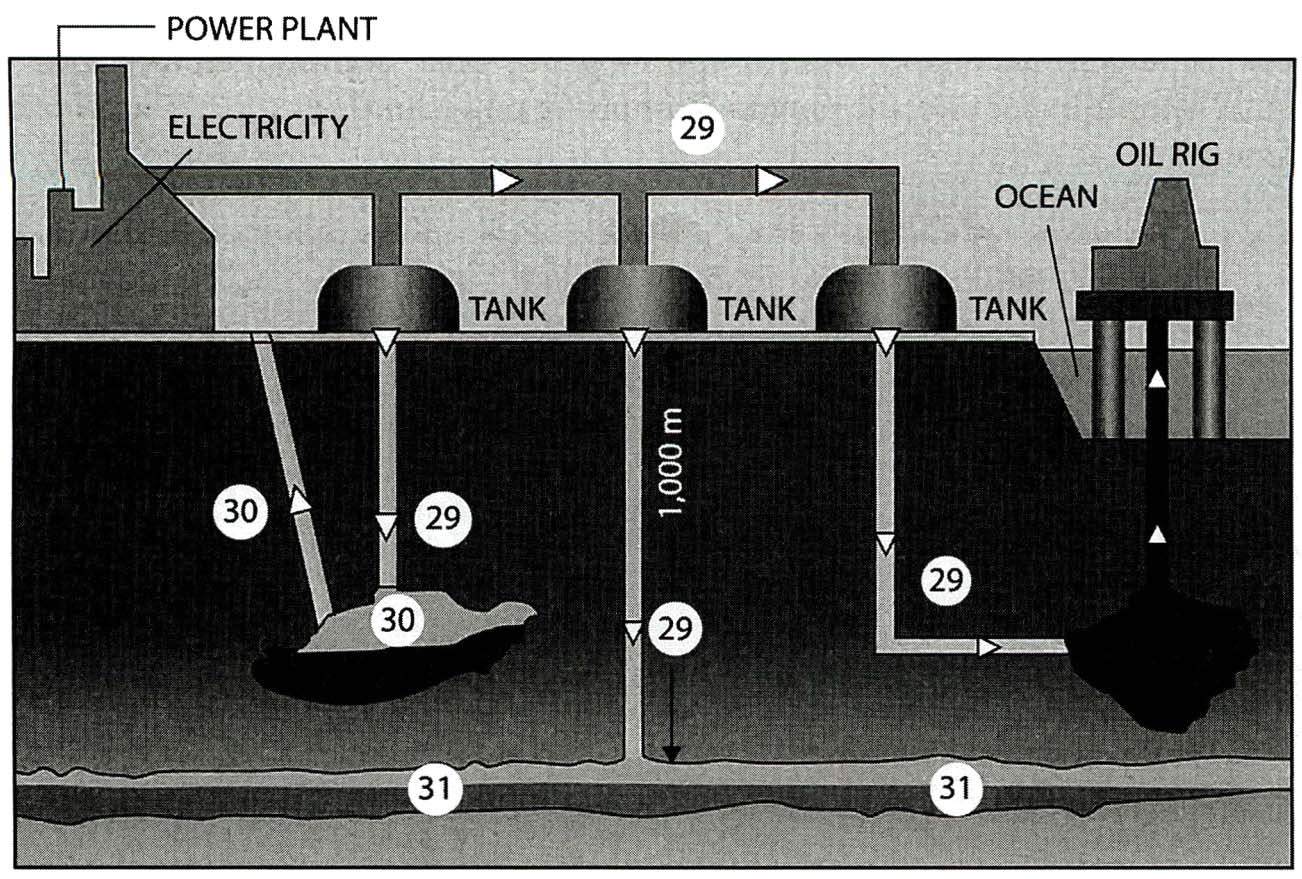
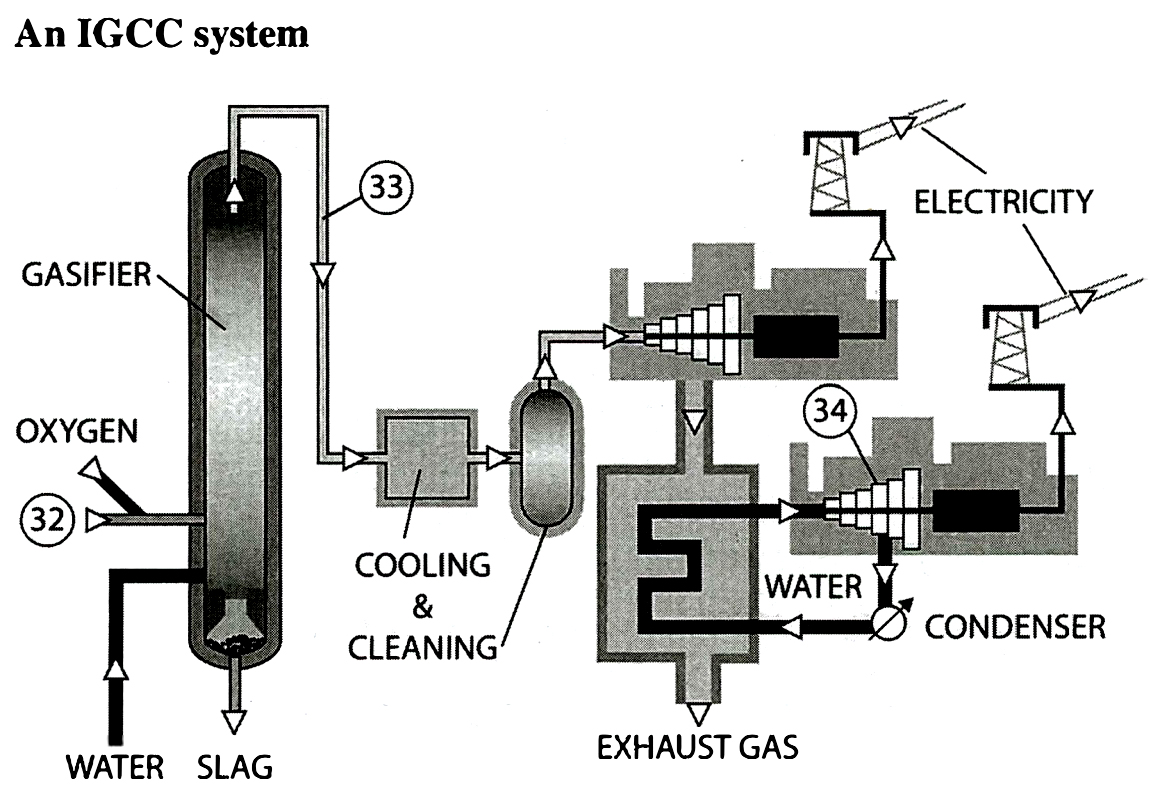
Label the diagrams on the following page.
Write the correct letter, A-H, in boxes 3-8 (IMAGE 29-34) on your answer sheet.
A CO2 B Coal C Natural gas
D Oil E Saline aquifer F Steam-driven turbines
G Syngas H Syngas-driven turbines
3. _________________
4. _________________
5. _________________
6. _________________
7. _________________
8. _________________
Carbon dioxide sequestration
Questions 9-14
Complete the table below.
Choose NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS AND/OR A NUMBER from the passage for each answer.
Write your answer in boxes 9-14 on your answer sheet.
|
Advantages of CCS |
Disadvantages of CCS |
|
Sequestration is already used in the oil and gas sector. CCS may cut 9._____________ in a short time. 10________________ in labour, |
The construction of new and the conversion of existing power plants and the liquefaction and transport of CO2 are very costly. While sequestration is possible, the scale would be enormous. Therefore, CCS would need 12.____________ |

Solution For:Carbon Capture And Storage Reading Answer
| 1. A | 8. F |
| 2. D | 9. carbon emissions |
| 3. A | 10. powerful lobbies |
| 4. C | 11. solar |
| 5. E | 12. massive state subsidies |
| 6. B | 13. untried |
| 7. G | 14. $0.0686/kWh |
Review and Practice
- Regularly practice with IELTS reading samples and time yourself to get used to the pressure of the exam.
- Review your mistakes to understand where you went wrong and how to avoid similar errors in the future.
Our Books
Master IELTS Speaking Part 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 Book
IELTS Writing Task 2 Book
Carbon Capture And Storage Reading Answer Explanation
Comin Soon
Practice IELTS Other Modules
IELTS Listening
The IELTS Listening test assesses how well you can understand spoken English in various contexts. It lasts about 30 minutes and is divided into four sections with a total of 40 questions. The listening tasks become increasingly difficult as the test progresses.
IELTS Academic Reading
The IELTS Academic Reading section assesses your ability to understand and interpret a variety of texts in academic settings. It is designed to evaluate a range of reading skills, including skimming for gist, reading for main ideas, reading for detail, understanding inferences, and recognizing a writer's opinions and arguments.
IELTS Speaking
The IELTS Speaking test assesses your ability to communicate in English on everyday topics. It lasts 11-14 minutes and consists of three parts: introduction, cue card, and a discussion based on the cue card topic.
IELTS General Reading
IELTS General Reading tests your ability to understand and interpret various types of texts. Here are some key areas and types of content you can expect to encounter in the reading section, along with tips for effective preparation.
IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 1, you are presented with a visual representation of information, such as graphs, charts, tables, or diagrams, and you are required to summarize, compare, or explain the data in your own words.
IELTS General Writing Task 1
In IELTS General Writing Task 1, you are required to write a letter based on a given situation. The letter can be formal, semi-formal, or informal, depending on the prompt. Here’s a breakdown of the key components to include in your letter
IELTS Academic Writing Task 2
In IELTS Academic Writing Task 2, you are required to write an essay in response to a question or topic. Here’s a guide to help you understand the essential elements of this task
IELTS Exam Tips
To succeed in the IELTS exam, practice regularly, familiarize yourself with the test format, improve your vocabulary, develop time management skills, and take mock tests to build confidence.
Grammer for IELTS
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication in English. Understanding tense usage, subject-verb agreement, and sentence structure enhances clarity and coherence in writing and speaking.
Vocabulary for IELTS
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in the IELTS (International English Language Testing System) exam, especially in the Speaking and Writing sections. Here’s an overview of why vocabulary is important and how it impacts your performance
RECENT IELTS SAMPLES QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
The Life And work Of Marie Curie Reading Answer
Marie Curie is probably the most famous woman scientist who has ever lived. Born Maria...
Becoming An Expert Reading Answer
A Expertise is commitment coupled with creativity. Specifically, it is the commitment of...
STUDY CENTRE COURSES Reading Answer
SELF-STUDY TIPS AHowever difficult you find it to arrange your time, it will pay off in the...
The Extrinct Grass In Britain Reading Answer
A The British grass interrupted brome was said to be extinct, just like the Dodo. Called...
Morse Code Reading Answer
A. A new satellite-based system is being implemented to replace Morse code for sending...
Magnetic Therapy Reading Answer
AMagnetic therapy, which is a $5-billion market worldwide, is a form of alternative medicine...